For ladies with dense breasts, new research findings present the adjunctive use of whole-breast ultrasound tomography (UST) gives higher breast most cancers detection than mammography alone.
For the retrospective multicenter research, not too long ago revealed in Radiology, researchers reviewed full-field digital mammography (FFDM) and UST information for 140 ladies (imply age of 56) with dense breasts. In line with the research, 36 ladies within the cohort had breast most cancers. The research authors famous that the 32 reviewing radiologists have been Mammography High quality Requirements Act-qualified radiologists with breast imaging expertise ranging between two and 37 years.
The researchers discovered that that the mix of FFDM and UST yielded an space beneath the curve (AUC) of 60 % for breast most cancers detection compared to 54 % for FFDM alone. Complete-breast ultrasound tomography does provide a few key benefits in breast most cancers screening, in line with the research authors.
Based mostly on the mammography views above (A) for a 60-year-old lady, 32 radiologists interpreted the pictures as revealing a BI-RADS 3 or decrease lesion. After reviewing full-field mammography in addition to ultrasound tomography slices (B), 17 of the 32 reviewing radiologists famous a BI-RADS 4 or increased presentation. Biopsy revealed a triple-negative invasive ductal carcinoma. (Pictures courtesy of Radiology.)
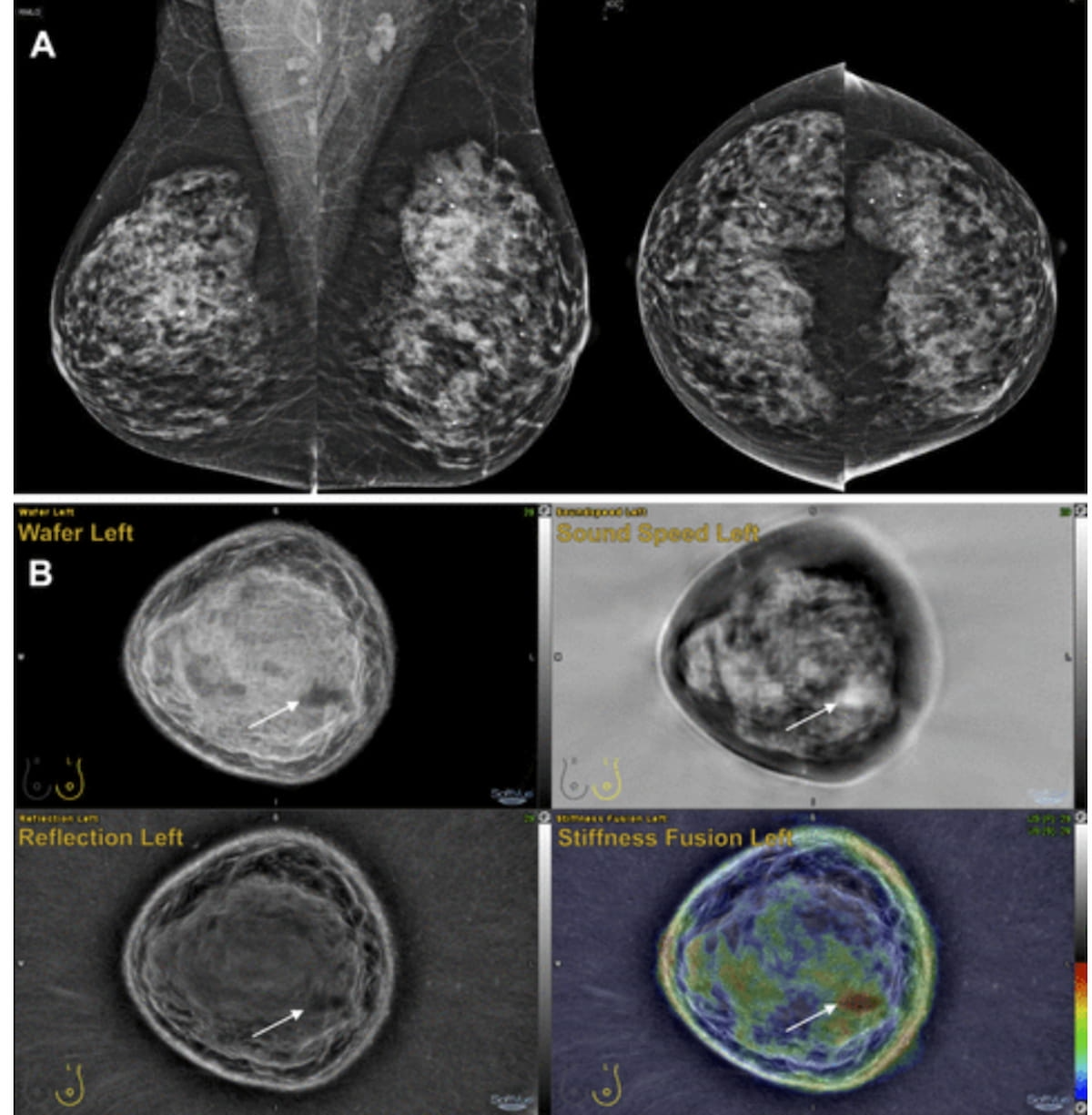
“First, coronal volumetric picture sequences are helpful to establish and characterize lesions. They supply a greater view of the fat-glandular interface the place most breast cancers are positioned. Second, the stiffness fusion sequence gives tissue stiffness info, which will help differentiate most cancers from benign plenty and isn’t available with handheld US or automated breast US,” wrote lead creator Mary W. Yamashita, M.D., a scientific professor of radiology and affiliate part chief of breast imaging on the Keck Faculty of Medication on the College of Southern California (USC), and colleagues.
For Breast Imaging Reporting and Information System (BI-RADS) 4 circumstances, the research authors famous that in distinction to FFDM alone, FFDM/UST had non-inferior specificity (82 % vs. 88 %) however provided superior sensitivity (37 % vs. 30 %). Nevertheless, in these circumstances, the researchers identified a web improve of 5.5 extra false constructive findings per reader.
“(The) addition of UST to FFDM resulted in solely a slight discount in constructive predictive worth in contrast with FFDM alone (42.2% vs 45.4%, respectively),” cautioned Yamashita and colleagues. “Medical research are wanted to find out whether or not supplemental UST can enhance most cancers detection with out considerably growing the variety of benign biopsies.”
Whereas the researchers noticed no statistically vital distinction with imply sensitivity in BI-RADS 3 circumstances (40 % for FFDM/UST vs. 33 % for FFDM alone), they discovered that FFDM/UST offered superior imply specificity (75 % vs. 69 %).
“The specificity enchancment with FFDM plus UST at BI-RADS 3 evaluation is encouraging. A BI-RADS 3 evaluation is the commonest supply of false-positive findings in handheld US and automatic breast us screening,” famous Yamashita and colleagues. “With improved BI-RADS 3 specificity, radiologists can extra precisely characterize plenty as benign (BI-RADS 2), resulting in fewer BI-RADS 3 assessments.”
Three Key Takeaways
1. Enhanced detection accuracy. Combining full-field digital mammography (FFDM) with whole-breast ultrasound tomography (UST) improves breast most cancers detection accuracy in ladies with dense breasts. The mixture yielded an space beneath the curve (AUC) of 60 %, in comparison with 54 % for FFDM alone.
2. Superior sensitivity in BI-RADS 4 circumstances. For BI-RADS 4 circumstances, FFDM mixed with UST confirmed superior sensitivity (37 % vs. 30 %) and non-inferior specificity (82 % vs. 88 %) in comparison with FFDM alone. This means that including UST will help establish extra cancers that may be missed by mammography alone, though it comes with a slight improve in false positives.
3. Elevated false constructive findings. Whereas the researchers famous the advantages of UST with respect to coronal volumetric picture sequences and stiffness fusion sequences, the addition of UST to FFDM resulted in a rise in false constructive findings. Particularly, there was a web improve of 5.5 extra false positives per reader. This concern highlights the necessity for scientific research to find out if the advantages of improved most cancers detection outweigh the drawbacks of elevated benign biopsies.
In an accompanying editorial, Ritse Mann, M.D., Ph.D, stated the elevated sensitivity with UST for BI-RADS 4 circumstances is consistent with earlier analysis taking a look at supplemental ultrasound however expressed reservation concerning the “poor general sensitivity” and probability of elevated false-positive findings.
“In my view, this research reveals that the present implementation for UST is at finest on par with handheld US and automatic breast US, permitting detection of some further cancers on the value of a considerable improve within the variety of false-positive findings. It appears that evidently UST could also be a brand new implementation of US, but it surely finally yields outdated outcomes,” maintained Dr. Mann, the chair of breast imaging on the Netherlands Most cancers Institute in Amsterdam and chair of the scientific and program committees of the European Society of Breast Imaging.
(Editor’s notice: For associated content material, see “Main Breast Radiologists Talk about the USPSTF Breast Most cancers Screening Suggestions,” “Complete Breast Ultrasound Screening: Is There Enough Utilization in Sufferers at Larger Danger for Breast Most cancers?” and “Breast Ultrasound Examine: AI Radiomics Mannequin Might Assist Predict Lymphovascular Invasion in Breast Most cancers Instances.”
In regard to review limitations, the authors conceded that reviewing radiologists obtained abbreviated scientific histories, had no prior imaging for sufferers and interpreted photographs in a laboratory setting for the research. The researchers additionally identified that the reviewing radiologists had no prior expertise with deciphering photographs from the breast ultrasound tomography (UST) system utilized within the research.

