Sufferers and outcomes
On this potential cohort research, 105 sufferers recognized and underwent cervical decompression surgical procedure for CSM had been recruited within the hospital. The inclusion standards had been as follows: (1) analysis per spinal cervical spondylosis; (2) present process decompression surgical procedure; (3) full follow-up information. The exclusion standards had been as follows: (1) sufferers with cervical backbone trauma; (2) sufferers with malignant tumors; (3) comorbid neurogenic illnesses; and (4) the presence of extreme dysfunction of important organs. Enrolled sufferers signed an knowledgeable consent. Baseline traits of the themes had been collected, together with affected person age, gender, BMI, vascular threat components (diabetes, smoking), and surgical process, and the affected person’s preoperative mJOA scores (Pre-mJOA) had been recorded and assessed.
All sufferers underwent cervical decompression surgical procedure, of which 81 sufferers underwent anterior cervical decompression and inner fixation (together with cervical disc substitute, subtotal cervical discectomy, and anterior cervical decompression and fusion), and 24 sufferers underwent posterior cervical decompression and inner fixation (together with laminectomy and laminoplasty).
On this research, the Modified Japanese Orthopedic Affiliation Rating(mJOA) [19] was used as a criterion for assessing the diploma of spinal twine neurologic impairment, with a traditional rating of 18, and the extra extreme the neurologic impairment, the decrease the rating. On this research, mJOA scores had been carried out preoperatively and one 12 months postoperatively in CSM sufferers, and restoration charges had been calculated. Postoperative restoration charge=(postoperative mJOA-preoperative mJOA)/(18-preoperative mJOA)×100% [20].Two teams had been divided in response to the dimensions of the restoration charge; restoration charge ≥ 50% was the great prognosis group, and < 50% was the poor prognosis group [21, 22].
Picture Acquisition
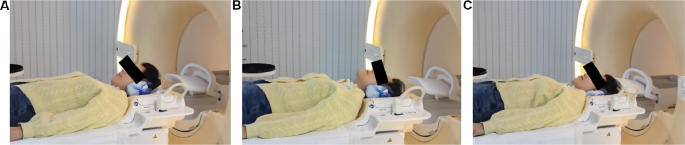
Typical Picture Acquisition: Preoperatively, Magnetic Resonance Imaging(MRI)was carried out on a Philips 3.0T dual-gradient superconducting magnetic resonance Ingenia-cx with an 8-channel head-neck mixed phased array floor coil to obtain the alerts. Sagittal T2WI, axial T2, and axial DTI (pure neck place, extension neck place, and flexion neck place) scans had been carried out. The sufferers had been scanned of their pure neck place within the supine place; for the flexion neck place scan, a pad was positioned below their necks to maintain their necks in flexion and to maintain the sternum and mandible close by; for the extension neck place scan, a pad was positioned below the affected person’s shoulders in order that the neck was prolonged posteriorly [9, 17] (Fig. 1). Axial T2 and DTI had been centered on the sagittal T2 picture to find out the narrowest neck place.
DTI Picture Acquisition: The imaging protocol consisted of the single-shot echo planar imaging (SS-EPI) sequence with the next parameters: the diffusion weighting issue b worth of 0 and 800s/mm²; the diffusion-sensitive gradient path was 15; the TR/TE was 2772/85ms; the layer spacing was 0; the layer thickness was 2.5 mm; the sphere of view was 224 × 224 mm; the matrix was 92 × 90, and NSA = 2.
Picture evaluation
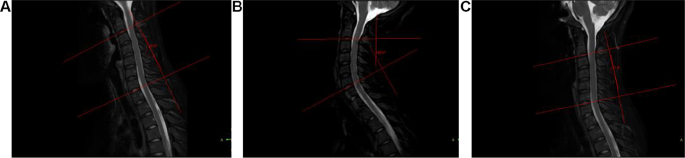
Typical Picture Evaluation: For processing, the photographs had been transferred to a Philips workstation: Nebula Workstation (IntelliSpace Portal) 9.0. Sagittal T2 pictures of the themes had been chosen, C2 and C7 lower-end plates had been used as tangent strains, the tangent strains had been used as perpendicular strains, and the intersection of the 2 vertical strains at an acute angle was referred to as the Cobb angle. The vary of movement (ROM) = Cobb angle in pure neck place – Cobb angle in flexion neck place, and the ROM in pure neck place was measured as proven in Fig. 2.
DTI Picture Evaluation: The pictures had been transmitted to the Neuro Perfusion workstation, and two senior radiologists made unbiased evaluations and choices. From the obtained DTI information, axial diffusivity (AD), radial diffusivity (RD), Imply diffusivity (MD), obvious diffusion coefficient (ADC), and fractional anisotropy (FA) maps had been generated. First, three eigenvalues(λ1, λ2, and λ3) and the eigenvectors had been calculated. Longitudinal diffusivity and RD had been outlined in equations from the directional diffusivity values obtained:
$$D{textual content{ }} = {lambda _1}$$
$$RD{textual content{ }} = {textual content{ }}({lambda _2} + {lambda _3}){textual content{ }}/{textual content{ }}2$$
$$start{aligned}ADC &= MD{textual content{ }} = {textual content{ }}({lambda _1} + {lambda _2} + {lambda _3}){textual content{ }}/{textual content{ }}3{textual content{ }} &= {textual content{ }}left({ADCx{textual content{ }} + {textual content{ }}ADCy{textual content{ }} + {textual content{ }}ADCz} proper){textual content{ }}/{textual content{ }}3end{aligned}$$
FA decided the diploma of anisotropy:
$$start{aligned}FA, =& ,sqrt {3({{[{lambda _1}, – ,MD]}^2}, + ,{{[{lambda _2}, – ,MD]}^2}, + ,{{[{lambda _3}, – ,MD]}^2})} &/sqrt {2(lambda _1^2, + ,lambda _2^2, + ,lambda _3^2)}finish{aligned}$$
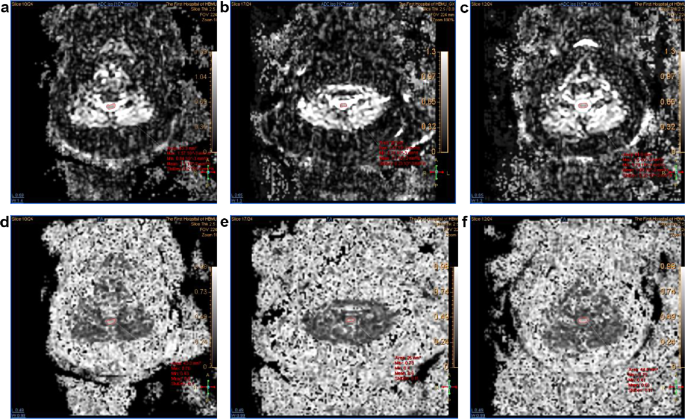
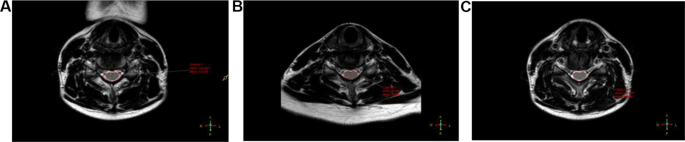
By checking the three-d area of curiosity (ROI), the utmost doable ROI was manually positioned on the twine with out together with cerebrospinal fluid. Probably the most severely compressed segments of the cervical spinal twine had been chosen. Their axial anisotropy rating maps and obvious diffusion coefficient maps had been reconstructed to stipulate the area of curiosity(ROI) within the middle of the spinal twine, fractional anisotropy (FA) and obvious diffusion coefficient (ADC) had been routinely created by the scanner in response to a deterministic fixed-step monitoring algorithm, utilizing diffusion. The orientation info described by the tensor was routinely created. The common of three measurements for every end result was used for statistical evaluation. DTI measurements had been taken as in Fig. 3. and the cross-sectional space of the spinal canal on the narrowest level was measured from the axial T2WI pictures in numerous positions, as in Fig. 4. The cross-sectional space of the spinal canal within the pure place, FA and ADC had been recorded as Space-N, ADC-N, and FA-N, respectively; of which extension neck place was recorded as Space-E, ADC-E, FA-E; of which flexion neck place was recorded as Space-F, ADC-F, FA-F.
Dynamic DTI measurement pictures of the CSM sufferers. (a: Obvious diffusion coefficient pictures of the neck in flexion place; b: Obvious diffusion coefficient pictures in extension place; c: Obvious diffusion coefficient pictures in pure place; d: Fractional anisotropy pictures in flexion place; e: Fractional anisotropy pictures in extension place; f: Fractional anisotropy pictures in pure place)
Statistical evaluation
Statistical evaluation was carried out utilizing SPSS (SPSS Statistics 27.0, IBM). The acquired information are introduced as imply ± normal deviation (SD) or percentages, and the normality of the info was checked with the Shapiro-Wilk check for the quantitative information. Variations in medical and traditional imaging traits and DTI parameters had been evaluated utilizing univariate evaluation to check the 2 teams by χ2 check, t-test, or Wilcoxon check. Variables with statistically vital variations had been analyzed by multivariable logistic regression, and the correlation between variables and outcomes was assessed individually for the totally different neck positions and described by odds ratios (OR), two-sided 95% confidence interval (95percentCI), and p-value (chance ratio statistics). The importance of the variables was assessed by checking the relevance of every p-value and evaluating the OR values. The forest plots had been constructed utilizing GraphPad Prism 9.5.1. The receiver working attribute (ROC) curve was drawn to calculate the area-under-the-curve (AUC) of CSM of various positions to guage the prediction efficiency of the pure, extension, and flexion place fashions. P < 0.05 was thought-about statistically vital.