MRI exhibits the results explicit danger components comparable to diabetes, air air pollution, and frequency of alcohol use have on “higher-order” mind areas situated within the cerebral cortex, researchers have discovered.
A workforce led by Jordi Manuello, PhD, of the College of Oxford within the U.Ok. reported that these danger components additional enhance a person’s vulnerability to situations comparable to schizophrenia and Alzheimer’s illness. The group’s findings have been printed March 27 in Nature Communications.
“[Our] outcomes present a complete image of the function performed by genetic and modifiable danger components on these fragile elements of the mind,” the authors famous.
Though earlier research have mapped a community of susceptible higher-order mind areas — that’s, areas that develop later in adolescence and present earlier degeneration as individuals age — precisely what the genetic influences on this fragile mind community stay unclear, the group defined. The workforce additionally wrote that it stays to be seen as as to whether affected person outcomes might be altered by addressing widespread modifiable danger components for situations comparable to schizophrenia or dementia.
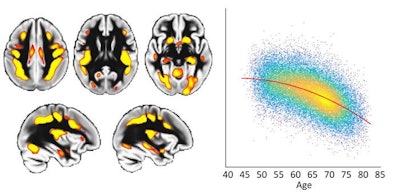 To the left of the determine, the red-yellow shade denotes the areas that degenerate sooner than the remainder of the mind and are susceptible to Alzheimer’s illness. These mind areas are higher-order areas that course of and mix data coming from our completely different senses. To the correct of the determine, every dot represents the mind knowledge from one UK Biobank participant. The general curve exhibits that, in these significantly fragile areas of the mind, there may be accelerated degeneration with age. Picture courtesy of Gwenaëlle Douaud, PhD, and Jordi Manuello, PhD.
To the left of the determine, the red-yellow shade denotes the areas that degenerate sooner than the remainder of the mind and are susceptible to Alzheimer’s illness. These mind areas are higher-order areas that course of and mix data coming from our completely different senses. To the correct of the determine, every dot represents the mind knowledge from one UK Biobank participant. The general curve exhibits that, in these significantly fragile areas of the mind, there may be accelerated degeneration with age. Picture courtesy of Gwenaëlle Douaud, PhD, and Jordi Manuello, PhD.
Manuello and colleagues performed a examine that included knowledge from 40,000 U.Ok. Biobank contributors over the age of 45 who underwent mind MR imaging. They assessed 161 components for dementia and ranked their affect on this susceptible mind community past the pure results of ageing. The danger components, dubbed “modifiable,” — as they are often modified all through an individual’s life — have been categorized into the next classes:
- Alcohol consumption
- Blood stress
- Ldl cholesterol
- Despair
- Diabetes
- Food regimen
- Schooling
- Listening to
- Irritation
- Bodily exercise
- Air pollution
- Sleep
- Smoking
- Socialization
- Weight
Total, the investigators discovered “important genome-wide associations between this mind community and 7 genetic clusters implicated in cardiovascular deaths, schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s illness, and with the 2 antigens of the XG blood group situated within the pseudoautosomal area of the intercourse chromosomes,” they reported.
The examine outcomes make clear a few of the “most crucial danger components for dementia and supply novel data that may contribute to prevention and future methods for focused intervention, mentioned senior writer Gwenaëlle Douaud, PhD, additionally of Oxford, in a press release launched by the college.
“Now we have discovered that a number of variations within the genome affect this mind community, and they’re implicated in cardiovascular deaths, schizophrenia, Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s illnesses, in addition to with the 2 antigens of a little-known blood group, the elusive XG antigen system, which was a completely new and sudden [discovery],” she mentioned.
The full examine might be discovered right here.

