Can a machine studying mixture of amyloid beta positron emission tomography (Aβ PET) and structural MRI (sMRI) improve differentiation between older wholesome management (OHC) individuals, these with delicate cognitive impairment (MCI) and sufferers with Alzheimer’s illness (AD)?
For the research, lately printed in Tutorial Radiology, researchers in contrast the one modalities sMRI and Aβ PET in addition to a machine studying mixture of the modalities of their overview of 261 research individuals. The cohort was comprised of 94 sufferers with AD (imply age of 69.62), 82 sufferers with MCI (imply age of 74.37) and 85 OHC (imply age of 70.76) individuals, in line with the research.
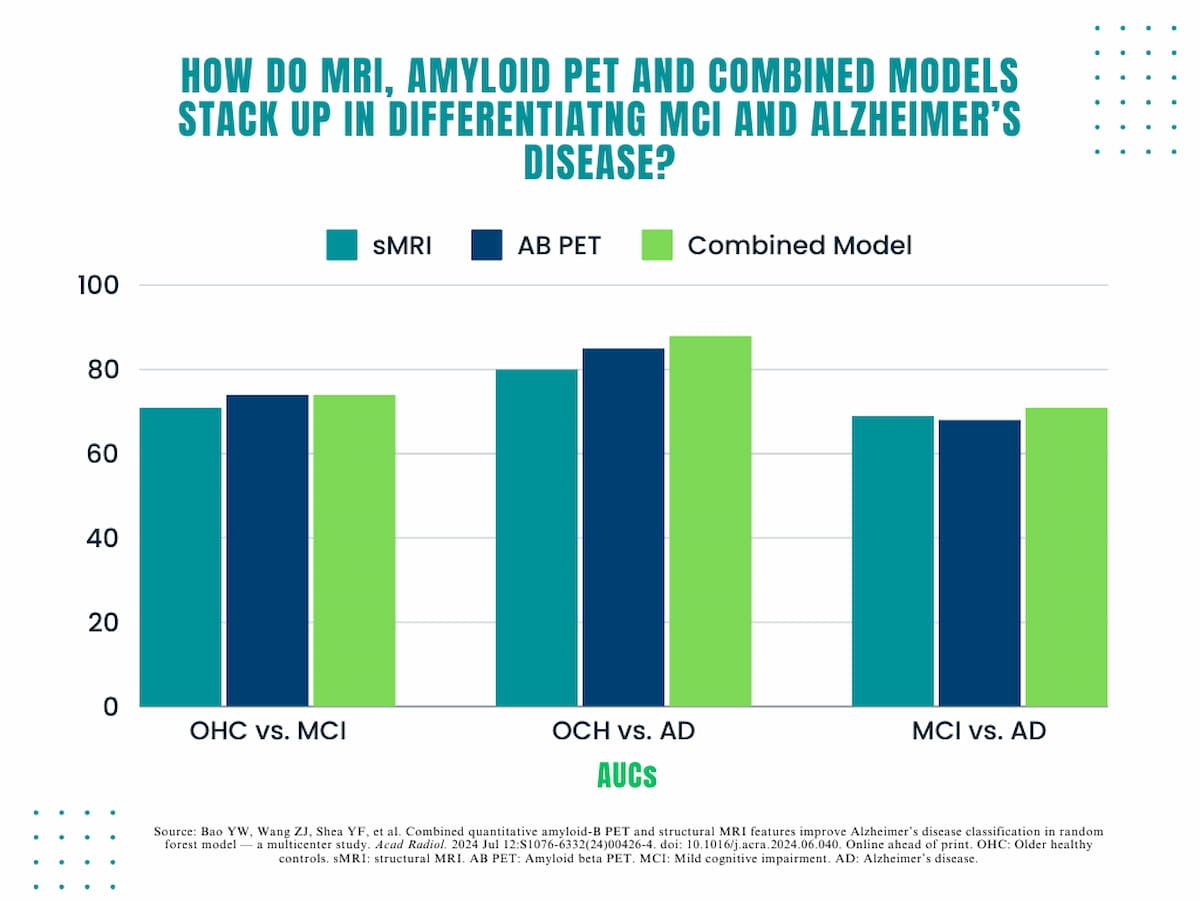
The research authors discovered an 81 p.c AUC for sMRI, an 86 p.c AUC for Aβ PET and an 89 p.c AUC for the mixed use of sMRI and Aβ PET options in differentiating between OHC and AD. The researchers famous the mix of sMRI/Aβ PET additionally demonstrated a 95 p.c sensitivity fee, an 89 p.c accuracy fee and an 80 p.c specificity fee for detecting AD.
In a brand new research, researchers discovered an 81 p.c AUC for sMRI, an 86 p.c AUC for Aβ PET and an 89 p.c AUC for the mixed use of sMRI and Aβ PET options in differentiating between older wholesome controls and people with Alzheimer’s illness.
“Our outcomes demonstrated Aβ distribution within the precuneus/posterior cingulate, lateral temporal and parietal cortex was simpler than different areas within the comparability between (OHC) and AD. The areas above are early affected by Aβ deposition within the hierarchical regional development sample from cognitively regular to AD, generally represented as stage I and II in line with Aβ staging,” wrote lead research writer Yi-Wen Bao, M.D., who’s affiliated with the Division of Medical Imaging on the Affiliated Huaian No. 1 Individuals’s Hospital of Nanjing Medical College in Jiangsu, China, and colleagues.
The researchers famous that the highest 10 options for differentiating between OHC and AD with the mixed use of modalities have been Aβ PET options with the parietal lobe’s amyloid load being the highest distinguishing function.
When evaluating the modalities in differentiating OHC versus MCI, the research authors discovered that larger accuracy (89 p.c) and sensitivity charges (95 p.c) with sMRI/Aβ PET. In addition they famous that the mixed mannequin had equal AUC (74 p.c) and accuracy charges (74 p.c) to Aβ PET imaging alone. For this a part of the evaluation, the research authors identified that sMRI options comprised the highest 10 options with cortical thickness of the left entorhinal cortex being the highest distinguishing function.
Three Key Takeaways
1. Enhanced differentiation with mixed modalities. The mixture of sMRI and Aβ PET imaging modalities considerably improves the differentiation between older wholesome management (OHC) individuals and Alzheimer’s illness (AD) sufferers in comparison with utilizing every modality alone. The mixed use demonstrated larger AUC (89%), sensitivity (95%), and accuracy (89%).
2. Prime options for differentiation. In differentiating OHC from AD, Aβ PET options, notably the amyloid load within the parietal lobe, have been probably the most distinguishing. For differentiating OHC from delicate cognitive impairment (MCI), sMRI options like cortical thickness of the left entorhinal cortex have been essential. The Aβ load within the left occipital lobe was a key distinguishing function between MCI and AD.
3. Implications of Aβ distribution and mind atrophy. The research signifies that mind atrophy is extra vital in classifying early phases of AD (like MCI) from OHC, whereas quantitative Aβ load is essential in distinguishing superior AD.
For the differentiation of MCI and AD, the mixed mannequin demonstrated a barely larger AUC (71 p.c) and accuracy fee (75 p.c) in distinction to both sMRI or Aβ PET alone, equal sensitivity to Aβ PET (95 p.c) and low equal specificity to sMRI (47 p.c). On this evaluation, the research authors mentioned the Aβ load of the left occipital lobe was the highest distinguishing attribute, and the remaining prime 10 options have been associated to regional Aβ PET.
“ … We speculate that mind atrophy will be extra vital within the classification between earlier phases of AD (corresponding to MCI) and OHC, however quantitative Aβ load might play a deciding function in differentiating superior AD from others as a result of function of Aβ in defining AD as a singular neurodegenerative illness,” maintained Bao and colleagues.
(Editor’s observe: For associated content material, see “Can Deep Studying Automate Amyloid Positivity Evaluation on Mind PET Imaging?,” “May MRI-Guided Ultrasound Facilitate Improved Discount of Amyloid-Beta Load in Sufferers with Alzheimer’s Illness?” and “Rising MRI and PET Analysis Reveals Hyperlink Between Visceral Stomach Fats and Early Indicators of Alzheimer’s Illness.”)
In regard to check limitations, the authors acknowledged a restricted cohort dimension and incomplete demographic info for a number of the research individuals. The researchers additionally conceded doable underestimation of AB uptake attributable to the usage of non-specific amyloid tracer binding in white matter and minor segmentation artifacts inside these areas.

