The examine design was accepted by the suitable ethics evaluate board, which waived the requirement for knowledgeable consent owing to the retrospective nature of the examine.
Affected person datasets
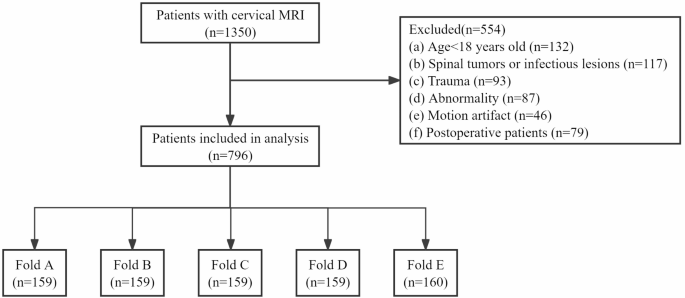
Sufferers with imaging-diagnosed degeneration between January 2016 and December 2018 had been chosen from the radiological reporting system of our hospital’s cervical backbone MRI database. In whole, 796 sufferers (imply age ± customary deviation, 51 years ± 10.06; males: 495, 63.57%) had been evaluated. Grownup sufferers (> 18 years previous) had been included within the examine. Sufferers had been excluded from the examine if that they had undergone instrumentation or introduced with different circumstances, corresponding to spinal tumors, infections, trauma, or scoliosis. Moreover, MRI information with important movement artifacts had been excluded to make sure acceptable high quality and reliability of the imaging evaluation (Fig. 1).
MRI
Cervical backbone MRI research had been carried out utilizing completely different MRI scanners (GE 1.5- and three.0-T platforms; Siemens 3.0 T platforms; United Imaging 3.0 T platforms), with the identical sequences and customary phased-array floor coils. Desk 1 gives particulars of the MRI scanners and sequences.
Knowledge set labeling
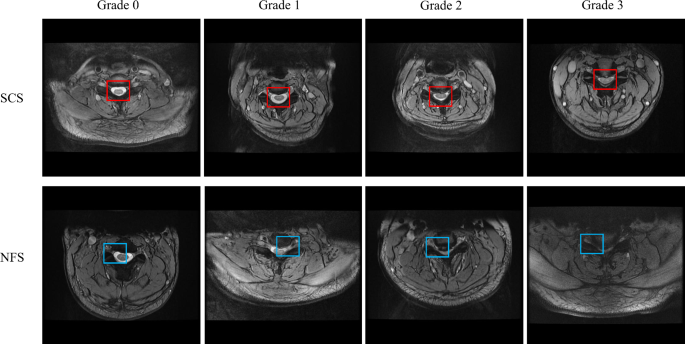
The info had been desensitized earlier than use to make sure that affected person info was not leaked. The uncooked information in customary Digital Imaging and Communications in Drugs (DICOM) format was used to make sure lossless information transmission. All personnel concerned in labeling had been required to obtain unified coaching and go a coaching evaluation previous to their qualification. All information had been annotated by 4 junior radiologists with ≥ 3 years of imaging expertise. After the information labeling was accomplished, it was reviewed and confirmed by two musculoskeletal radiology consultants with > 20 years of expertise, and the constant opinions of the 2 consultants had been thought-about the diagnostic reference label. Every radiologist was blinded to the affected person demographics and scientific historical past. Utilizing open-source annotation software program, bounding containers had been drawn to section the ROIs (central canal and neural foramina) at and between every cervical disc degree. When drawing every bounding field, the annotating radiologist categorized the cervical stenosis. The grading system for the severity of stenosis was primarily based on transverse T2 weighted imaging (WI) findings and categorized in accordance with the next standards: Grading system for SCS: Grade 0, no stenosis; Grade 1, Delicate stenosis with lower than 50% obstruction; Grade 2, Average stenosis characterised by spinal canal narrowing with spinal twine deformation however with out sign modifications throughout the spinal twine; and Grade 3, Extreme stenosis with narrowing accompanied by excessive sign depth throughout the spinal twine. Grading system for NFS: Grade 0, no stenosis; Grade 1, Delicate stenosis, the place the fats surrounding the nerve root is obstructed by < 50% of the nerve root circumference, with no morphological modifications to the nerve root; Grade 2, Average stenosis with obstruction of the fats surrounding the nerve root exceeding 50% of the nerve root circumference, with out morphological modifications to the nerve root; and Grade 3, Extreme stenosis manifesting as collapse of the nerve root. Grading was carried out utilizing well-established standards for CSS on the central canal and neural foramina [19,20,21,22] (Fig. 2) (Desk 2). 4 junior radiologists independently evaluated the MRI photographs to find out the presence or absence of spinal stenosis. The beginning and finish instances of every doctor’s analysis of every picture had been additionally recorded.
Improvement of the DL mannequin
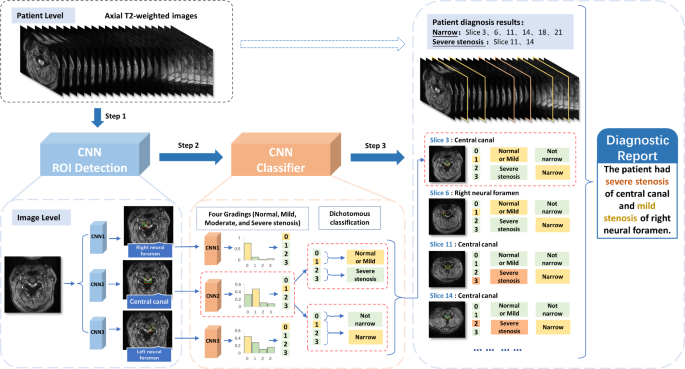
A technique for diagnosing cervical spinal stenosis was proposed primarily based on the DL mannequin (Quicker R-CNN) [18], consisting of an ROI detection module and cascade classification prediction. First, three sorts of CNNs had been used to detect the ROIs in several elements of the cervical MR photographs (the left neural foramen, proper neural foramen, and central canal). The picture options of the ROIs extracted by the CNNs had been then fed to the total connection layer (regular, gentle, reasonable, and extreme) for classification. Cascade classification was subsequently carried out to foretell the CSS standing of every affected person slice. Lastly, the outcomes had been mixed to acquire a patient-level diagnostic report (Fig. 3). The general cascading course of design was seamlessly built-in with the processing workflow of the DL fashions.
After experimental comparability, the optimizer for the DL fashions used Stochastic Gradient Descent with an preliminary studying charge of 0.02 Every mannequin was skilled for 50 epochs, and the educational charge adjustment technique was chosen as StepLR, which was up to date each 5 epochs, with a gamma of 0.5. The loss operate is a composite of ROI detection, which was calculated utilizing the Intersection over Union (IoU) of the bottom fact and predicted bounding containers, and classification losses, which was calculated utilizing a four-class focal loss operate for classification.
Statistical evaluation
All of the statistical analyses had been carried out utilizing SPSS model 23 software program (IBM Corp., Armonk, NY, USA). Steady variables are expressed as imply ± customary deviation, whereas categorical variables are expressed as frequencies and ratios. Cohen’s κ check was carried out to find out the consistency between the DL mannequin outcomes and junior radiologist annotated outcomes, offering Cohen’s κ coefficient and its 95% confidence interval. The DL mannequin was developed in Python (model 3.8) and PyTorch (model 1.8.1).
The efficiency was evaluated primarily based on the accuracy (ACC), space below the curve (AUC), sensitivity, specificity, F1 rating, prognosis time used for classification, and recall charge for ROI detection localization. To find out the presence of a big distinction between the AUC values, we used the DeLong check. IoU was used to measure the diploma of overlap between the expected and annotated areas. IoU > 0.5 is taken into account an inexpensive prediction end in most common instances, and the positioning of the ROIs is correct. To make sure full information utilization and keep away from the impression of an uneven information distribution, the same five-fold cross-validation was adopted to check the analysis metrics, which might additionally confirm the robustness of the DL mannequin. All of the check outcomes had been averaged over 5 random partitions that lined one another. One was chosen because the check set for every division, and the opposite 4 had been chosen because the coaching set. All analysis metrics had been calculated as the typical of 5 completely different divisions.