The usage of gadolinium ethoxybenzyl-diethylenetriaminepentaacetic acid (Gd-EOB-DTPA) enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) presents the most effective sensitivity for detecting neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases (NETLMs), in response to a brand new comparative examine.
For the retrospective examine, just lately printed within the European Journal of Radiology, researchers in contrast Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI with polyenergetic computed tomography (CT) and dual-layer spectral detector CT (DLCT) for the detection of NETLM. The examine cohort was comprised of 72 sufferers with suspected NETLM who had belly DLCT and Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI exams. Out of 477 recognized lesions, the examine authors famous that 396 lesions have been metastatic.
The researchers discovered that Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI provided a 95 % sensitivity charge for diagnosing NETLM compared to 86 % for DLCT and 76 % for polyenergetic CT. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI additionally had a per-lesion space beneath the curve (AUC) of 97 % in distinction to 91 % for DLCT and 86 % for polyenergetic CT, in response to the examine authors.
Right here one can polyenergetic CT (A), monoenergetic CT at 40 keV (B) and MRI photos (C-F) for a 63-year-old man with neuroendocrine tumor liver metastases. Whereas the polyenergetic CT confirmed no definitive metastatic lesion, the monoenergetic CT prompt a subcapsular proper lobe metastasis and T2-weighted and diffusion-weighted MRI revealed a excessive sign and apparent enhancement within the arterial section. (Photos courtesy of the European Journal of Radiology.)
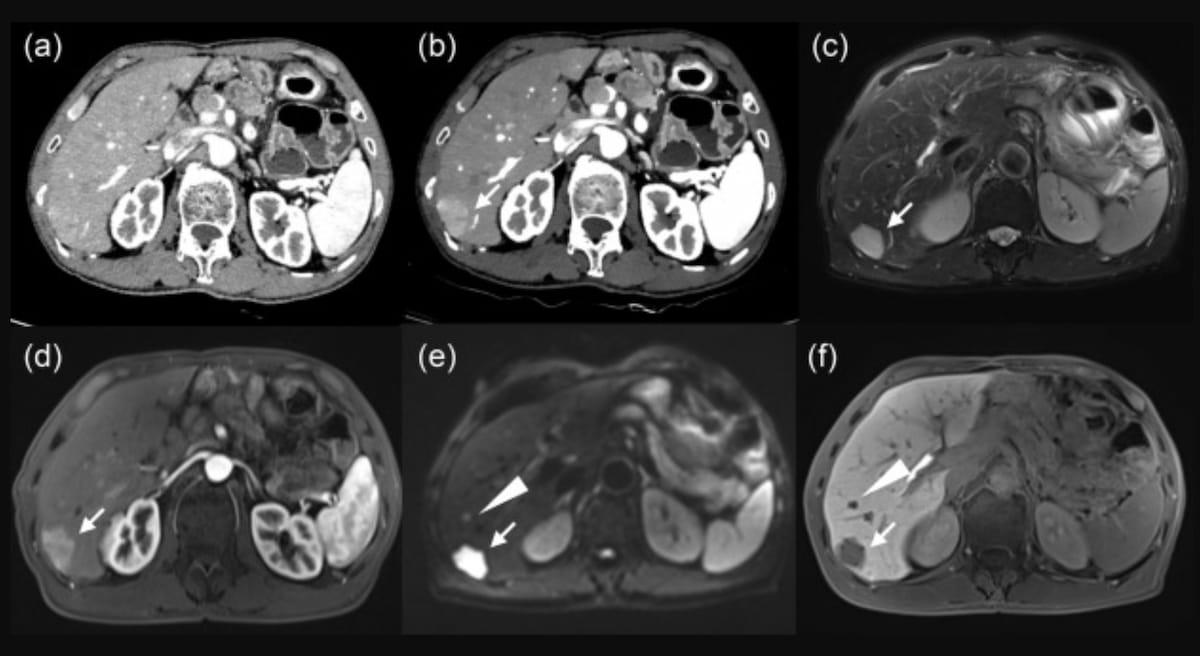
“The a number of practical imaging sequences (characterize) the primary benefit of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR. (Neuroendocrine tumors are) pathologically characterised by excessive mobile density and nuclear/cytoplasmic quantity ratio, and diffusion of water molecules is extremely restricted inside the tumor. Because of this, DWI is extremely delicate to NETLM detection,” wrote lead examine writer Tiansong Xie, M.D., who’s affiliated with the Division of Radiology on the Fudan College Shanghai Most cancers Middle in Shanghai, China, and colleagues.
Whereas there have been no vital variations between the imaging modalities for NETLM lesions > 10 mm, the examine authors identified that Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI had a considerably larger sensitivity charge for NETLM lesions < 10 mm (94 %) compared to DLCT (80 %) and polyenergetic CT (66 %).
“The (hepatobiliary section) of the Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MR has been reported to exhibit greatest tumor–liver interface and highest (contrast-to-noise ratio) CNR in NETLM detection in comparison with different sequences,” added Xie and colleagues.
Three Key Takeaways
1. Greater sensitivity for small lesions. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI confirmed a considerably larger sensitivity (94 %) for detecting NETLM lesions smaller than 10 mm in comparison with dual-layer spectral detector CT (80 %) and polyenergetic CT (66 %).
2. Superior diagnostic accuracy. Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI achieved a 95 % sensitivity charge and a 97 % space beneath the curve (AUC) for diagnosing NETLM, outperforming DLCT (86 % sensitivity, 91 % AUC) and polyenergetic CT (76 % sensitivity, 86 % AUC).
3. Limitations of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI. Whereas Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI presents superior tumor-liver interface imaging and better contrast-to-noise ratio (CNR), its use is proscribed by excessive prices, time-consuming acquisition, and potential inaccuracies in sufferers with liver dysfunction, notably these present process chemotherapy for liver metastases. These components could have an effect on its scientific utility in sure affected person populations.
Nevertheless, the researchers cautioned that along with the excessive value and time-consuming acquisition of Gd-EOB-DTPA-enhanced MRI, this imaging modality could be adversely affected by liver dysfunction in sufferers at the moment being handled with chemotherapy for liver metastases.
The examine authors additionally famous that digital monoenergetic imaging at 40 kiloelectron voltage (keV) provided a better signal-to-nose ratio (SNR) and CNR compared to polyenergetic CT. Within the arterial section, the researchers famous the usage of VMI at 40 keV greater than doubled the SNR in distinction to polyenergetic CT (16.28 vs. 7.85) and greater than tripled the CNR (5.49 vs. 1.47).
(Editor’s be aware: For associated content material, see “MRI Precisely Levels Cervical Neuroendocrine Carcinoma,” “New Radiopharmaceutical Provides Higher Tumor Imaging and Staging for Sufferers with Liver Most cancers” and “Rising Mannequin with Key MRI Function Improves Prediction for Superior Recurrence of Hepatocellular Carcinoma.”)
In regard to review limitations, the authors famous the retrospective examine design and a reference customary based mostly on imaging interpretation and pathological info. The researchers additionally famous potential affected person choice bias with respect to excessive suspicion of liver metastases in sufferers who had DLCT and Gd-DTPA-enhanced MRI exams.

