Exterior validation testing of an rising deep studying (DL) nomogram revealed considerably enhanced accuracy, specificity, and optimistic predictive worth (PPV) in preoperative prediction of tumor deposits in sufferers being handled for rectal most cancers.
For the retrospective examine, lately printed in Tutorial Radiology, researchers in contrast a medical mannequin (primarily based on magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)-detected T stage and lymph nodes), a 30-feature DL mannequin and a nomogram that mixed DL and medical elements for predicting tumor deposits in 529 sufferers who had radical surgical procedure for rectal most cancers.
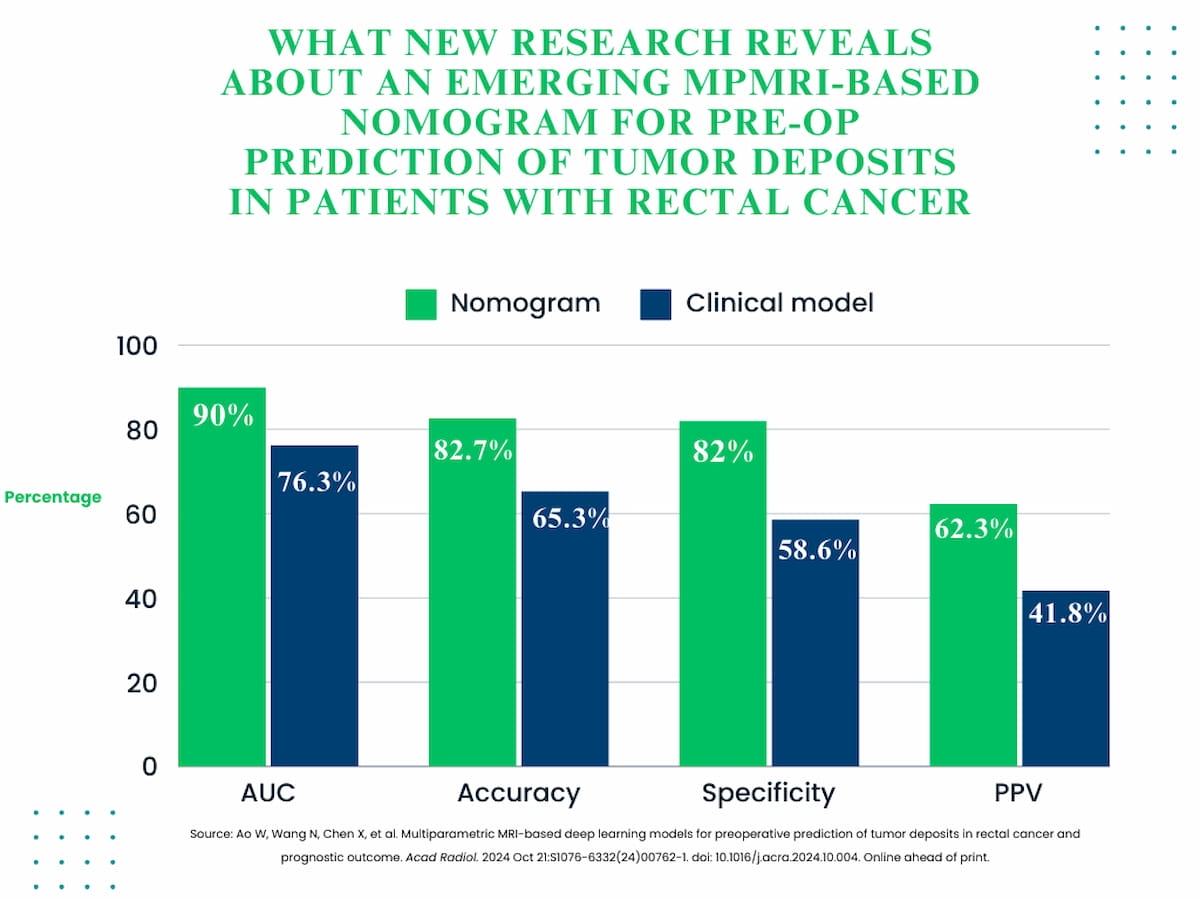
In exterior validation testing, the nomogram demonstrated considerably greater capability for predicting tumor deposits than the medical mannequin with respect to space underneath the curve (AUC) (90 % vs. 76.3 %), accuracy (82.7 % vs. 65.3 %), specificity (82 % vs. 58.6 %) and optimistic predictive worth (PPV) (62.3 % vs. 41.8 %).
In exterior validation testing, a nomogram that mixes deep studying and medical elements demonstrated considerably greater capability for predicting tumor deposits in sufferers with rectal most cancers than the medical mannequin with respect to space underneath the curve (AUC), accuracy, specificity and optimistic predictive worth (PPV).
“One potential clarification is that (tumor deposit) is extra prevalent in sufferers with domestically superior (rectal most cancers), and deep studying options derived from such instances could present important variations in radiomic traits in comparison with early-stage instances,” wrote lead examine creator Weiqun Ao, M.D., who’s affiliated with the Division of Radiology on the Tongde Hospital of Zhejiang Province in Hangzhou, China, and colleagues.
Whereas multiparametric MRI (mpMRI) performs a key position in defining tumor biology and prognostic analysis of sufferers with rectal most cancers, the researchers famous challenges with the heterogenous nature of perirectal fats lesions and overlap between the shows of tumor deposits and non-tumor deposit lesions.
Three Key Takeaways
1. Enhanced prediction accuracy with deep studying (DL) nomogram. Combining MRI-based medical elements with a 30-feature DL mannequin, the nomogram considerably improved predictive accuracy (82.7 % vs. 65.3 %) and specificity (82 % vs. 58.6 %) over the medical mannequin in figuring out tumor deposits in rectal most cancers.
2. Prognostic worth for disease-free survival (DFS). Each the DL mannequin and nomogram efficiently differentiated between high- and low-risk teams for three-year DFS, not like the medical mannequin, indicating their potential in evaluating prognosis in sufferers with rectal most cancers.
3. Potential influence on medical decision-making. The DL mannequin and nomogram demonstrated superior capacity to determine sufferers at greater danger for recurrence, which might support clinicians in making extra knowledgeable remedy choices. By precisely figuring out high-risk sufferers, these instruments could assist personalize therapeutic methods and enhance outcomes in rectal most cancers administration.
Emphasizing that tumor deposits are sometimes related to decrease survival in sufferers with rectal most cancers, the examine authors famous the medical mannequin did not differentiate between sufferers at high- and low-risk for three-year disease-free survival (DFS) at one of many two taking part facilities within the examine.
“In distinction, each the DL mannequin and the nomogram efficiently differentiated between high- and low-risk sufferers with distinct DFS profiles, demonstrating superior predictive capabilities,” identified Ao and colleagues. “Moreover, making use of the DL mannequin and the nomogram in predicting 3-year DFS outcomes helps their potential position within the prognostic analysis of (rectal most cancers).”
(Editor’s be aware: For associated content material, see “Rectal Most cancers MRI: Seven Key Takeaways from a New Literature Assessment,” “Diffusion-Weighted MRI and Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy for Rectal Most cancers: What New Analysis Reveals” and “Hybrid MRI Deep Studying Mannequin Reveals Promise in Predicting Tumor Deposits with Rectal Cancer.”)
In regard to review limitations, the authors acknowledged the opportunity of affected person choice bias given the examine’s exclusion of sufferers who had preoperative neoadjuvant remedy. The researchers additionally famous the dearth of evaluation for tumoral and peritumoral options.

