Rising analysis means that reassessment of breast magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) recognized as high-risk by synthetic intelligence (AI) might result in considerably improved detection of early breast most cancers.
For the retrospective research, just lately printed in Tutorial Radiology, researchers evaluated the aptitude of a convolutional neural community, skilled on breast MRI, for predicting the event of breast most cancers inside a 12 months of detrimental breast MRI outcomes. Drawn from a dataset of three,029 MRI from 910 sufferers (imply age of 52), the cohort was comprised of 115 circumstances of breast most cancers recognized on MRI. All sufferers had an preliminary BI-RADS evaluation of < 3, based on the research.
For the prediction of breast most cancers inside one 12 months, the researchers discovered that the AI mannequin had a 72 % space underneath the receiver working attribute curve (AUC). For preliminary MRI scans, there was a visible correlation in 83 of 115 circumstances that progressed to biopsy-proven breast most cancers, based on the research authors, who added that almost all of visible correlates had been < 0.5 cm.
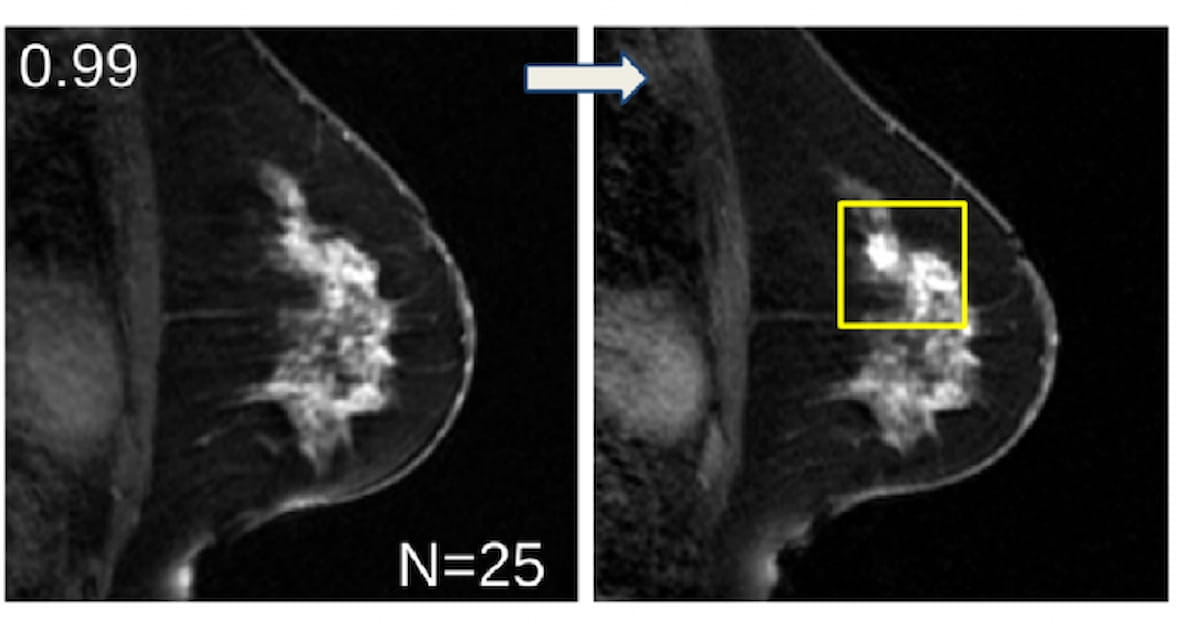
Right here one can see a real constructive case of breast most cancers with a view of a wholesome breast MRI (left) and AI-selected slice with a 99 % prediction at one 12 months for breast most cancers growth. The following MRI (proper) with a radiologist-selected slice reveals localized breast most cancers. (Photos courtesy of Tutorial Radiology.)
The researchers additionally emphasised that reassessment of breast MRIs recognized as high-risk by the AL mannequin might have led to upward of a 30 % enchancment in early detection of breast most cancers.
“It is very important be aware right here that the sensitivity of 30% reported listed here are for cancers that might have remained in any other case undetected till the subsequent examination. They’re extra cancers above and past people who have already been detected with excessive sensitivity by the radiologist,” wrote lead research creator Lukas Hirsch, Ph.D., who’s affiliated with the Metropolis Faculty of New York in New York, N.Y., and colleagues.
Noting present constructive predictive worth (PPV) benchmarks of 15 % for tissue prognosis and 4.4 % for irregular interpretation, the research authors stated the aforementioned 30 % sensitivity could be related to a 6 % PPV for reassessment of MRI scans deemed at high-risk by the AI mannequin.
Three Key Takeaways
1. AI-enhanced early detection. The reassessment of breast MRIs flagged as high-risk by an AI mannequin might result in a 30 % enhance in early breast most cancers detection, serving to determine circumstances that may have gone undetected till the subsequent screening.
2. Improved localization. The AI mannequin precisely recognized the long run location of breast most cancers in 57 % of circumstances, which may help radiologists in pinpointing areas for nearer examination and follow-up.
3. Enhanced constructive predictive worth (PPV). By re-evaluating AI-identified high-risk MRIs, radiologists may doubtlessly enhance the detection of clinically vital tumors by no less than 15 %.
“If radiologists recalled solely half of those re-evaluated circumstances, they might approximate the really useful PPV for tissue prognosis, and detect no less than an extra 15% of tumors, which is a clinically significant enchancment,” maintained Hirsch and colleagues.
The research authors additionally famous that the AI mannequin appropriately recognized the placement of future breast most cancers in 66 of the 115 circumstances (57 %). For 35 true constructive circumstances, the researchers maintained that the AI mannequin appropriately recognized the localization of breast most cancers in 25 circumstances (71 %).
(Editor’s be aware: For associated content material, see “Can Multimodal AI Improve Prediction of Axillary Lymph Nodes Past MRI or Ultrasound-Primarily based Fashions?,” “AI Mammography Platform Reveals Promising Outcomes for Detecting Subclinical Breast Most cancers” and “Enhancing Lesions on Breast MRI: Can an Up to date Kaiser Scoring Mannequin Enhance Detection?”)
Past the inherent limitations of a single-center retrospective research, the authors acknowledged the evaluation of MRI being restricted to sagittal scans and conceded the small variety of screen-detected breast cancers.

