Analysis continues to help the usage of magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) in breast most cancers screening for ladies deemed to be at high-risk for breast most cancers, together with these with dense breasts.
Listed below are 5 key takeaways from a brand new literature overview, which was lately revealed in Insights into Imaging.
1. In 15 research revealed between 2000 and 2015 taking a look at imaging modalities for ladies with a hereditary predisposition to breast most cancers, researchers discovered that contrast-enhanced breast MRI had a sensitivity fee ranging between 71 to 100%. Compared, the sensitivity fee ranged between 48 to 67 % for the mix of mammography and ultrasound, between 33 and 52 % for ultrasound, and between 25 to 58 % for mammography.
2. In a 2019 research analyzing a decade of MRI surveillance for over 4,500 girls at excessive threat of breast most cancers (together with 954 BRCA1 carriers and 598 BRCA2 carriers), researchers discovered that 185 invasive carcinomas and 36 instances of ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) had been detected inside 12 months of annual screening.
Researchers discovered that abbreviated breast MRI had a 57 % larger sensitivity fee for breast most cancers (96 %) than digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) (39 %) in a research of 1,444 girls with heterogeneously dense or extraordinarily dense breasts. (Picture courtesy of Radiology.)
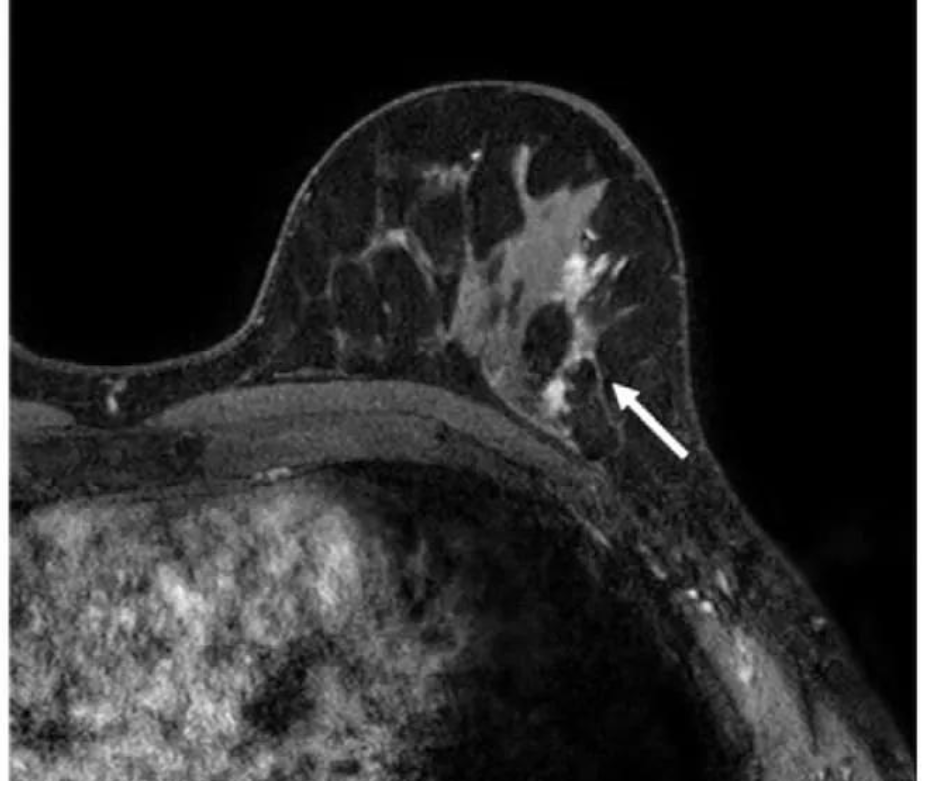
3. Researchers discovered that abbreviated breast MRI had a 57 % larger sensitivity fee for breast most cancers (96 %) than digital breast tomosynthesis (DBT) (39 %) in a research of 1,444 girls with heterogeneously dense or extraordinarily dense breasts. The research authors additionally famous that DBT had a ten % larger specificity than abbreviated breast MRI (97 % vs. 87 %) and a 17 % larger optimistic predictive worth (PPV) (36 % vs. 19 %).
4. In a randomized managed trial involving 1,355 girls at high-risk for breast most cancers, researchers discovered that the median invasive most cancers detected with MRI was 9 mm compared to a median tumor dimension of 17 mm identified with mammography.
5. Magnetic resonance imaging demonstrated superior leads to breast most cancers detection (1.52 per 1,000 screenings) compared to DBT, handheld ultrasound and automatic breast ultrasound in a 2023 meta-analysis involving 132,166 girls with dense breasts and adverse findings on mammography exams.

